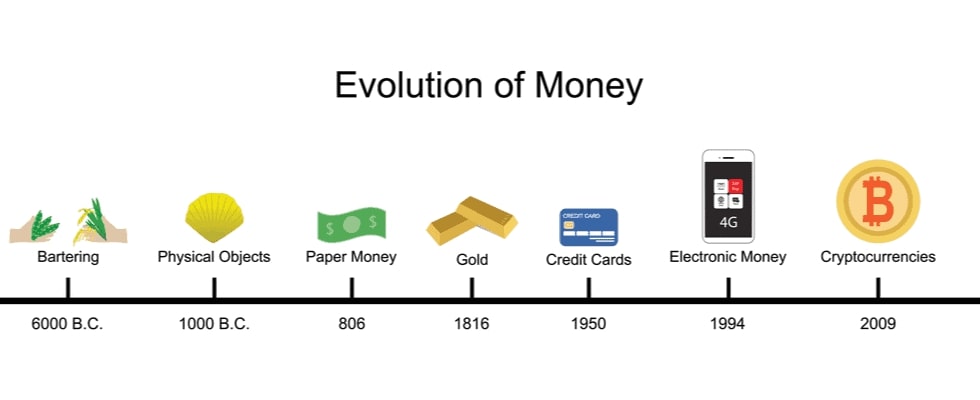
Currency plays a vital role in every economy — past, present, and future. From primitive trade systems to sophisticated digital payments, the evolution of money tells the story of civilization itself. In this post, we’ll explore the history of currency and how it continues to shape our world today.
Part 1: The Origins – From Barter System to Metal Coins
1. The Barter System: Where Money Began
Before coins and bills, people relied on bartering — exchanging goods and services without a standard medium. While effective in small communities, this system was limited by its reliance on mutual needs and immediate trade.
2. Commodity Money: Trading with Value
As societies advanced, they began using commodity money — items like salt, tea, shells, and cattle — which held intrinsic value. This early form of currency was more versatile and widely accepted than bartering.
3. The First Coins: The Rise of Metal Currency
The world’s first minted coins appeared in Lydia around 600 BCE, crafted from electrum. Coinage revolutionized trade by offering a standardized, durable, and portable form of money. Ancient Greece, Rome, and China soon adopted their own coin systems, spreading monetary culture across continents.
Part 2: The Rise of Paper Currency and Modern Systems
4. Paper Money in Ancient China
China introduced paper money during the Tang Dynasty (7th century) and fully adopted it under the Song Dynasty. Lighter and more convenient than coins, this innovation gradually influenced the rest of the world over centuries.
5. Banking and Centralized Currency Systems
The growth of commerce led to the emergence of banks, enabling safe storage and exchange of money. By the 17th century, central banks were established to issue national currencies and control inflation. The Bank of England was one of the first to set a model for modern banking.
6. National Currencies and the Gold Standard
In the 19th century, countries adopted national currencies tied to the gold standard — a system where money was backed by gold reserves. This brought trust and stability to global markets, setting the stage for modern financial systems.
Part 3: Digital Era and the Future of Currency
7. The Digital Revolution in Finance
Today, we live in a cashless society powered by debit cards, mobile apps, online wallets, and e-banking. Digital currency is now mainstream, allowing instant transactions across borders without physical cash.
8. Cryptocurrency: The New Frontier
The launch of Bitcoin in 2009 changed the way we think about money. Based on blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies offer decentralized, transparent, and secure methods of exchange. While volatile, they hint at a future beyond traditional banking systems.
🌍 Evolution of Currency: From Barter to Paper Money
🔁 Barter System – The Origin of Trade
In the earliest days of human civilization, people practiced bartering, exchanging goods and services directly without using money.
Barter allowed individuals to trade their surplus for what they needed, fostering local trade and cooperation.
However, the barter system had limitations:
- No common measure of value
- Difficulty finding a “double coincidence of wants” (both parties needing what the other offered)
These challenges led to the search for a more efficient medium of exchange.
🐚 Commodity Money – The First Universal Currency
To overcome the drawbacks of bartering, societies began using commodity money—items with intrinsic value that were widely accepted in trade.
Examples include:

- Cowry shells
- Salt
- Livestock
Commodity money acted as the first standardized currency, providing a durable and universally recognized store of value.
Coins & Precious Metals – A Trusted Medium of Exchange
As trade expanded, precious metals like gold and silver emerged as preferred forms of money due to their rarity, durability, and inherent value.
Key advancements included:

- Standardized weights and measures
- Minting of coins bearing the seal of an authority
Coinage brought trust and consistency to transactions, laying the foundation for modern currency systems.
💴 Paper Money – Portable & Practical
With growing economies and increasing trade, the need for a more portable and divisible currency led to the creation of paper money.

✅ First recorded use: 7th century A.D. in China
✅ Initially backed by precious metal reserves
✅ Issued by governments and central banks
Paper currency became a convenient alternative, offering:
- Lightweight handling
- Easy division for small and large transactions
- Increased efficiency in both local and international trade
Conclusion: Where Is Currency Headed?
The journey of History of currency reflects humanity’s progress — from simple trade to global economies interconnected through technology. As we move deeper into the digital age, money is becoming smarter, faster, and more global than ever before.
Whether it’s ancient coins, paper bills, or cryptographic assets, one truth remains: currency is essential to human connection and commerce. Understanding its history helps us better prepare for its future.







